Marketplaces as a Growth Channel in International Trade: Platforms and Opportunities Recap
In recent years, marketplaces have moved from the sidelines to the driver’s seat for international brands and manufacturers. For many companies, these platforms are now a faster path to new markets than building an e-commerce store from scratch or negotiating distribution deals with local partners.
But marketplaces are not magical vending machines where you upload a product and watch orders roll in. They are complex ecosystems with their own algorithms and deadly competition.
In this article, I’ll break down the key marketplaces and show how to promote your products there without gambling with your budget.
What Is a Marketplace in Plain English?
It is an online platform that connects sellers and buyers while handling the heavy lifting: traffic, payments, logistics, and sometimes customer support. Unlike your own online store:
-
Sellers don't need to generate traffic from scratch.
-
The platform already has demand.
-
You compete for visibility rather than clicks.
Classic examples of marketplaces are well-known Amazon, eBay, and Allegro.
Choose Your Fighter: Types of Marketplaces
1. Product-based: The most common and straightforward type. Buyers visit these marketplaces ready to shop, while the platform connects brands with end consumers.
Key features:
-
Focus on price, delivery, and ratings;
-
Strong competition between sellers.
-
Sales depend on SEO, content, and logistics.
-
Purchase decisions are made quickly.
Examples: Amazon and AliExpress.
2. Service-based: These platforms sell services or expertise rather than goods. Buyers choose not a product, but rather a person or team to perform a task.
Key features:
-
The result or competence is sold.
-
Profiles and reviews play a key role.
-
The decision-making cycle is longer.
-
There is less automation and more human involvement.
Examples: Upwork and TaskRabbit.
3. Peer-to-peer (P2P) marketplaces: On these platforms, people sell directly to other people. The platform does not fully control the product; it creates an environment for the transaction.
Key features:
-
Low entry threshold.
-
Uneven quality of goods.
-
Trust is formed through seller ratings.
-
More freedom and fewer standards.
Examples: Etsy and Facebook Marketplace.
4. B2B marketplaces that are designed for transactions between companies. Here, companies sell not individual goods, but rather batches, contracts, and production capabilities.
Key features:
-
Wholesale, contracts, and white label.
-
Long transaction cycle.
-
Reputation and verification are important.
-
The focus is on partnerships rather than quick sales.
Examples: Alibaba and Global Sources.
Global Marketplaces That Run the World
Not all marketplaces are equally global. Some operate across many countries and connect you with buyers worldwide. The big advantage is that you can sell internationally without opening companies everywhere — you can use their existing infrastructure.
Below, I will review the most common global marketplaces using data from SimilarWeb.
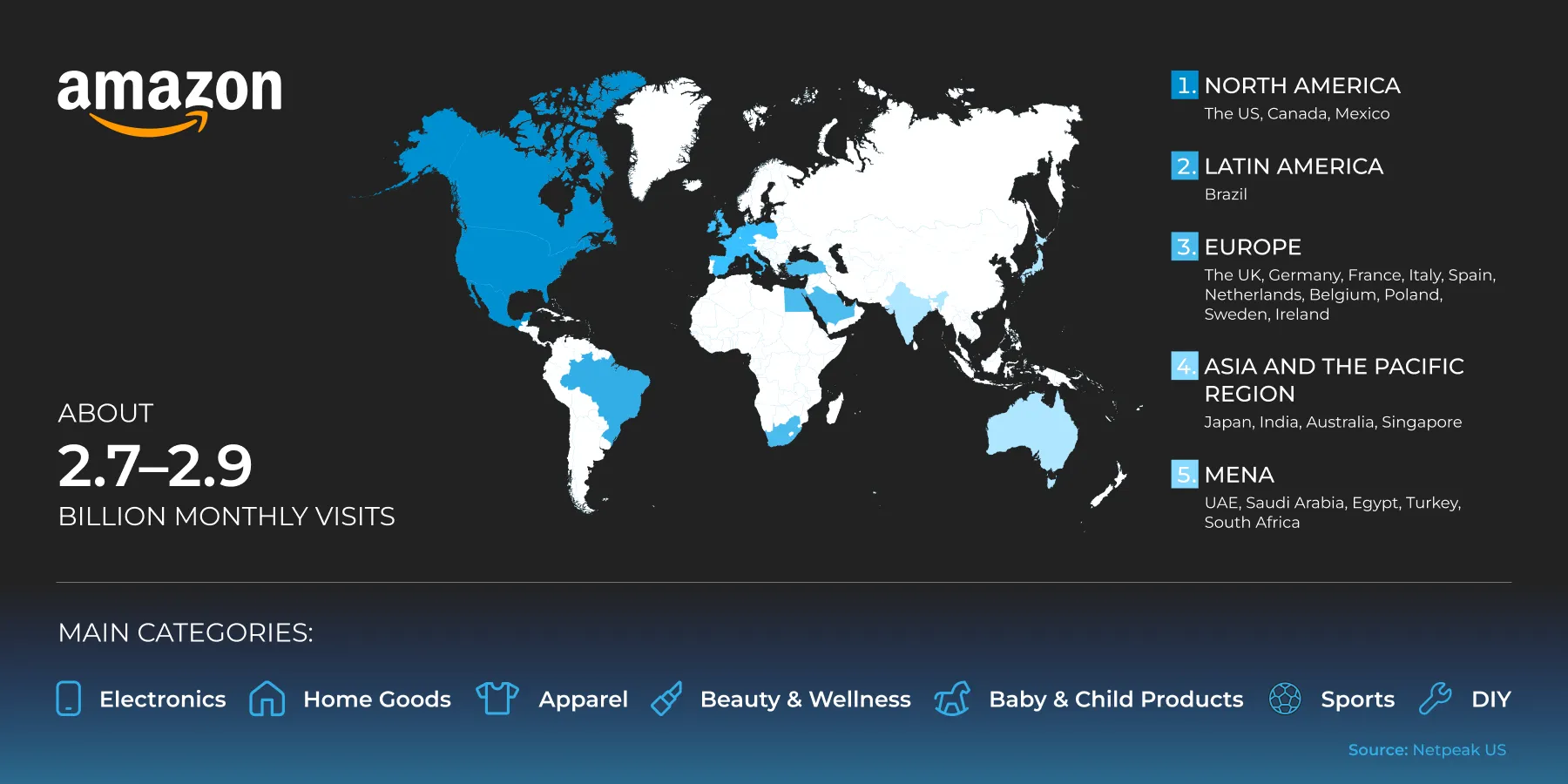
Amazon
Amazon is the world's largest marketplace ecosystem. Its features include robust logistics (FBA), advanced advertising, strict rules, and intense competition. It is suitable for systematic scaling.
Coverage regions:
-
North America: USA, Canada, and Mexico.
-
Latin America: Brazil.
-
Europe: United Kingdom, Germany, France, Italy, Spain, the Netherlands, Belgium, Poland, Sweden, and Ireland.
-
Asia and the Pacific: Japan, India, Australia, and Singapore.
-
MENA: UAE, Saudi Arabia, Egypt, Turkey, and South Africa.
There are approximately 2.7–2.9 billion visits per month.
Main categories: Electronics, home goods, clothing, cosmetics and personal care products, children's products, sports equipment, and DIY supplies.
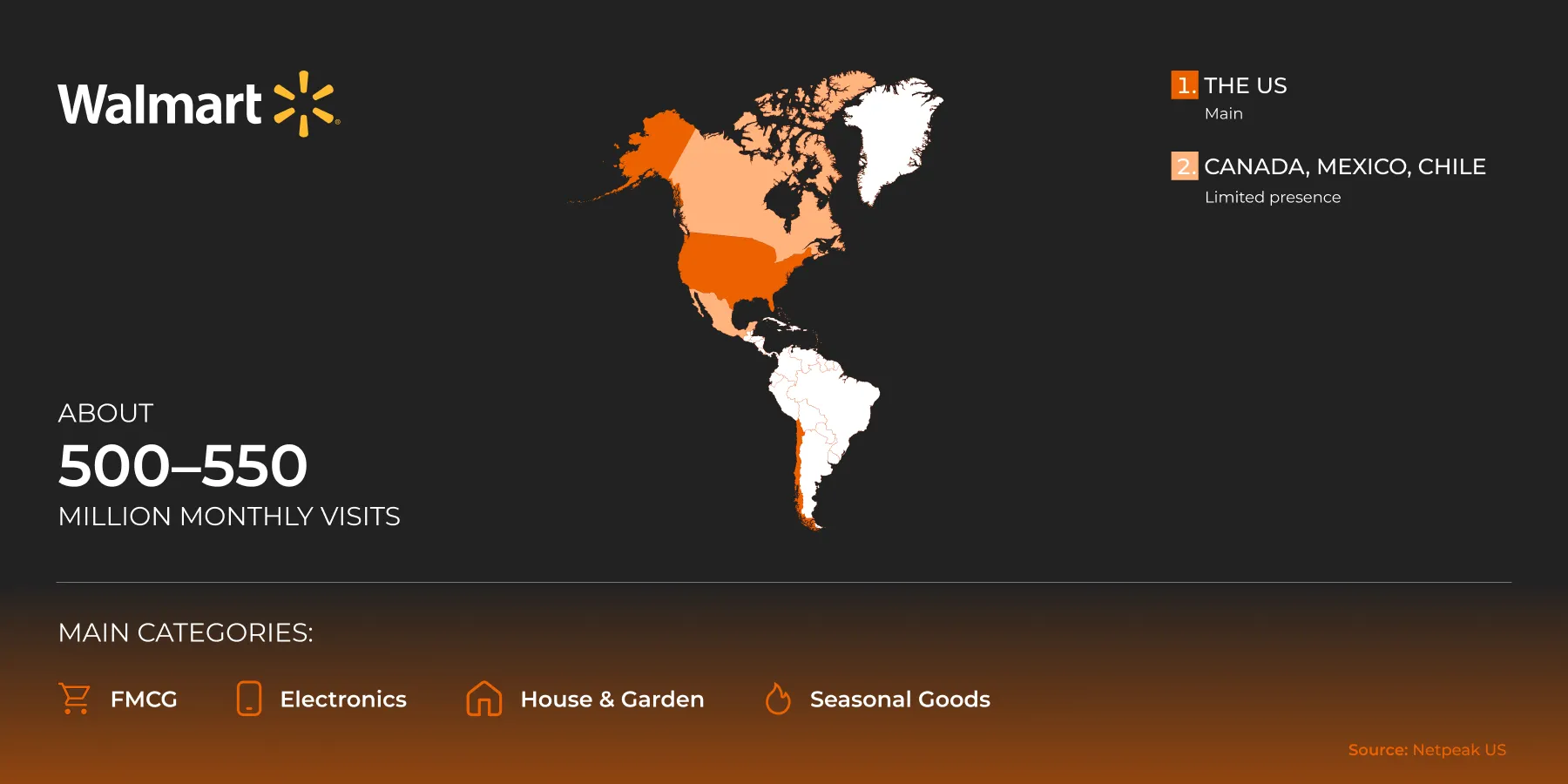
Walmart
Walmart has strong offline and online brand recognition and high credibility in the US. It is more difficult to enter, has strict moderation, and focuses on price competitiveness.
Coverage regions: US (main) and limited coverage in Canada.
Walmart has separate marketplace projects in Mexico and Chile, but Walmart Marketplace mainly serves US sellers.
It receives approximately 500-550 million visits per month.
Main categories: Fast-moving consumer goods (FMCG), electronics, home and garden, and everyday and seasonal goods.
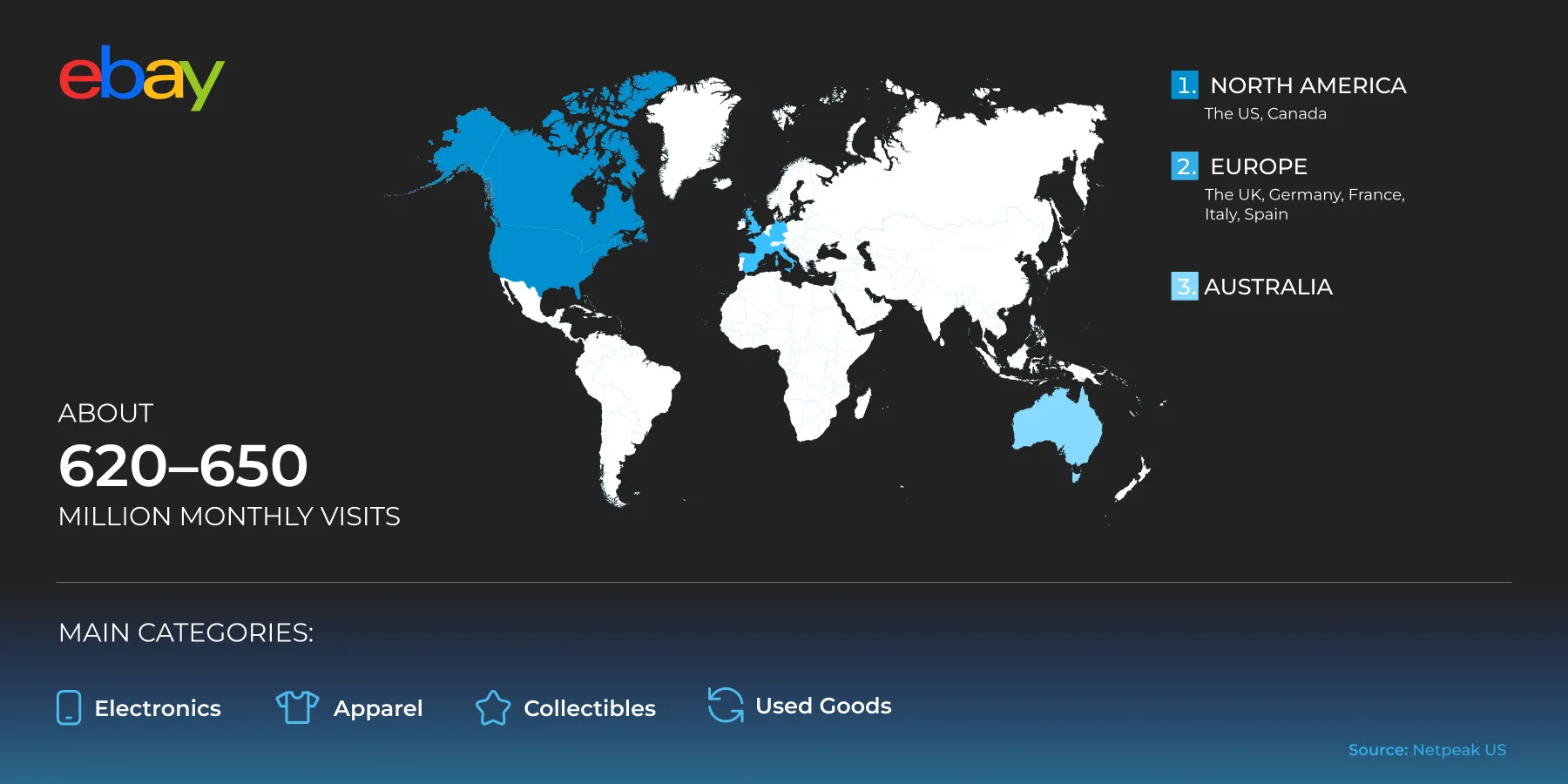
eBay
eBay has a hybrid C2C and B2C model, and is well-suited for cross-border sales. There are fewer brand restrictions and more freedom, which works well for niche and resale categories.
Coverage regions:
-
North America: US and Canada.
-
Europe: United Kingdom, Germany, France, Italy, Spain.
-
Australia.
There are approximately 620–650 million visits per month.
Main categories: Electronics, auto parts, clothing, collectibles, used items, and vintage items.
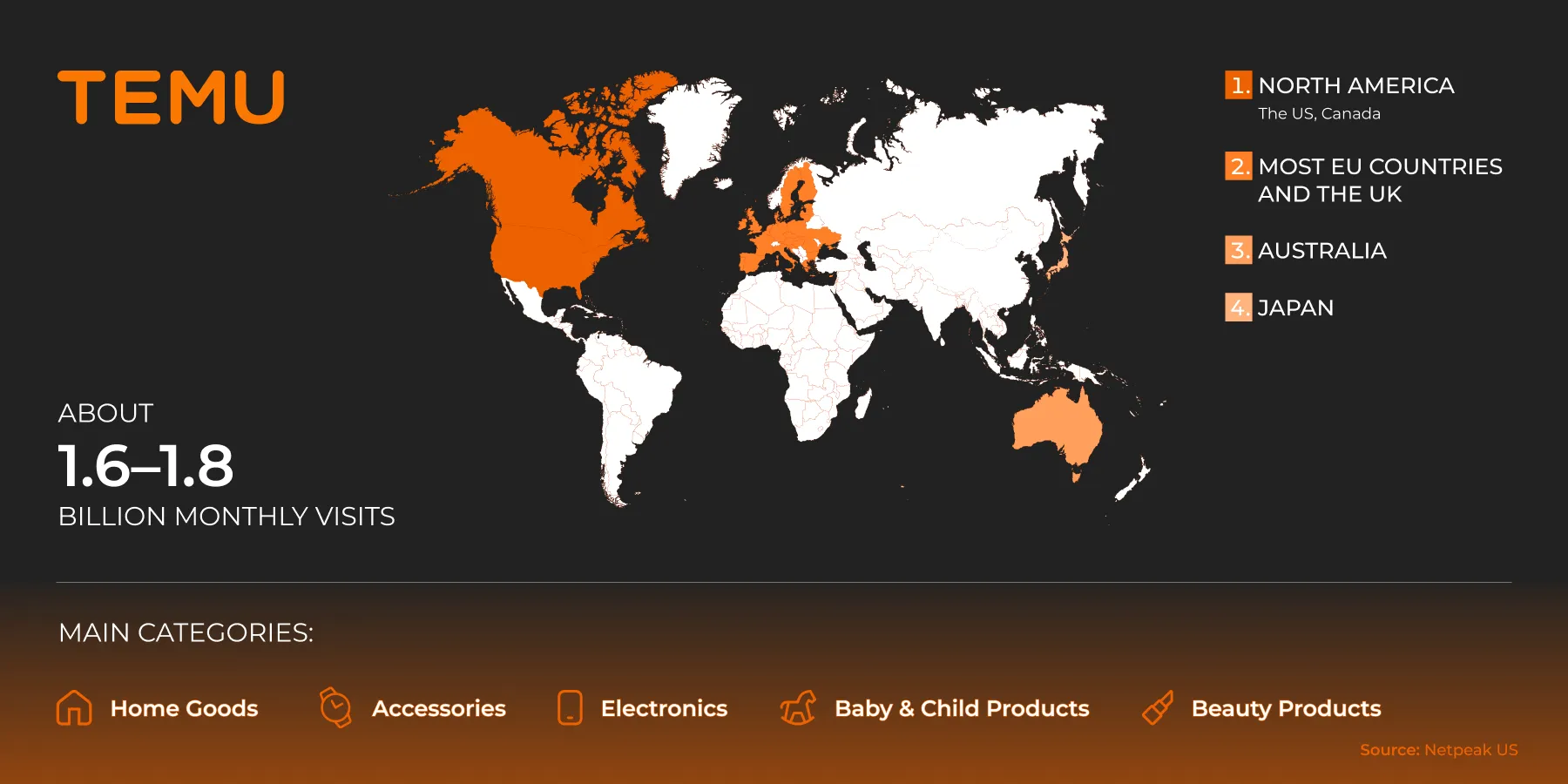
Temu
Temu is known for its aggressive pricing, substantial advertising budgets, and control over its platform. It does not allow products to be priced higher than on other marketplaces. While it is suitable for high volumes, there are limited opportunities for brand promotion.
Coverage regions:
-
North America: USA and Canada.
-
Most EU countries and the UK.
-
Australia and Japan.
-
Japan.
There are approximately 1.6–1.8 billion visits per month.
Main categories: Home, accessories, clothing, small electronics, children's products, and cosmetics.
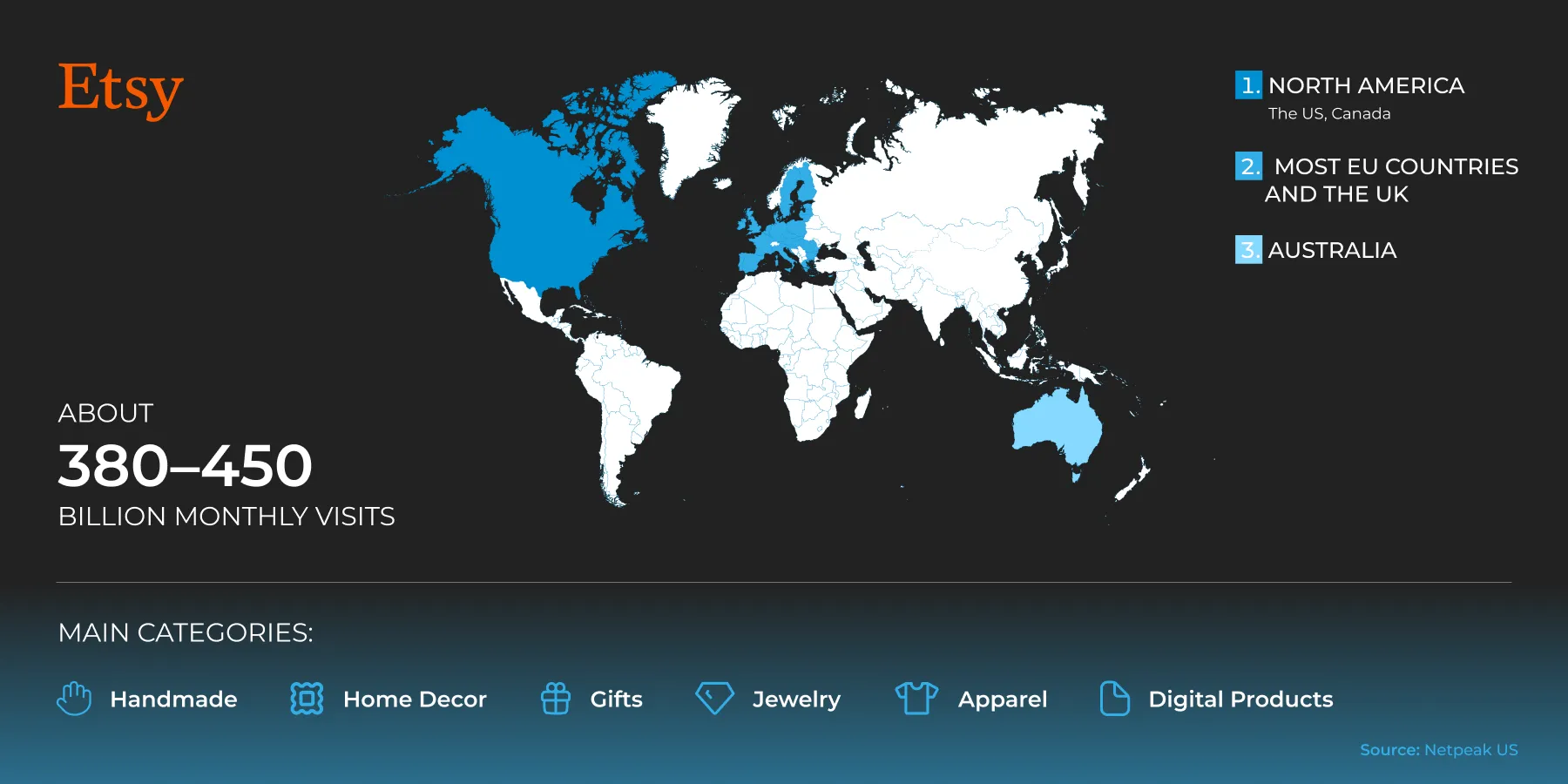
Etsy
Etsy is a niche marketplace with strong organic traffic. It is not suitable for mass-market goods because content, storytelling, and brand identity play a major role.
Coverage regions:
-
North America: USA and Canada.
-
Great Britain and EU countries.
-
Australia.
There are approximately 380–450 million visits per month.
Main categories: Handmade items, décor, gifts, jewelry, clothing, and digital goods.
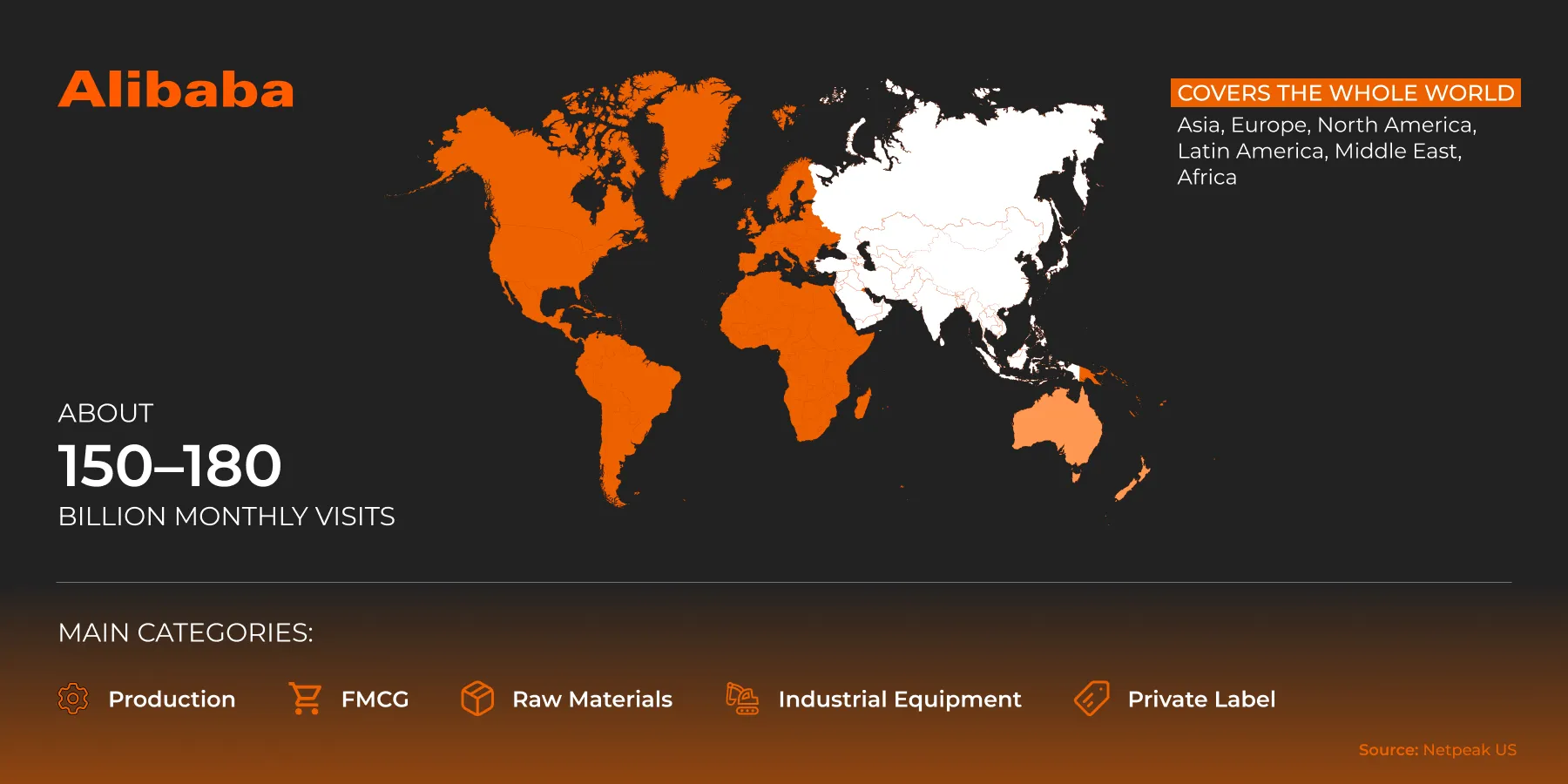
Alibaba
Alibaba has a B2B focus with long transaction cycles, wholesale, contracts, and exports. It is a key platform for manufacturers and white-label products.
It covers the entire world. Main regions covered: Asia, Europe, North America, Latin America, the Middle East, and Africa.
It receives approximately 150–180 million visits per month.
Main categories: Manufacturing, FMCG, raw materials, industrial equipment, and private label.
Local Marketplaces That Run Countries
In many countries, one local marketplace becomes the default place to shop online. And often, these homegrown platforms influence how people buy, what they expect from sellers, and whom they trust more than global players.
Below, I will review several major platforms in Europe and worldwide.
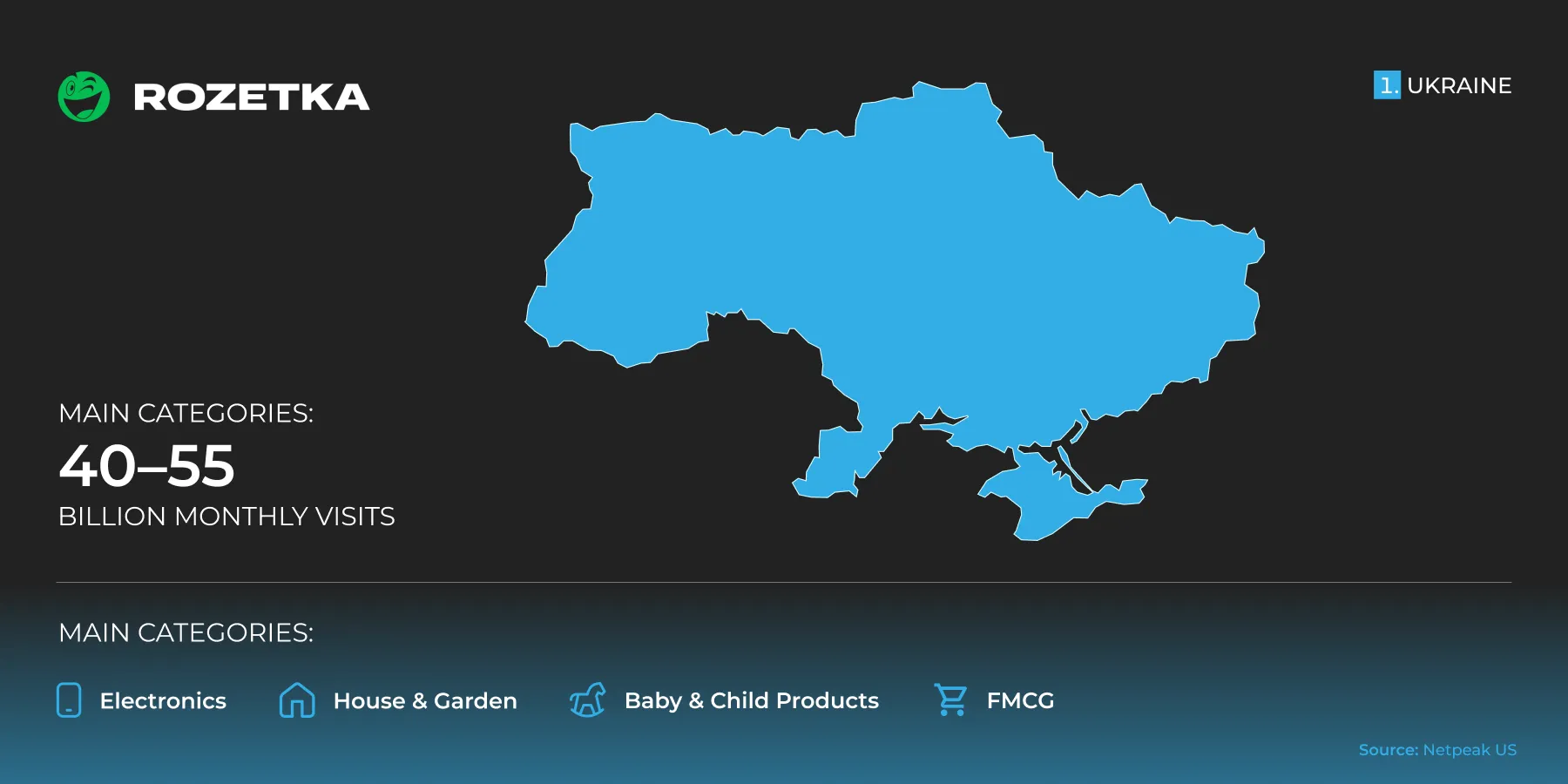
ROZETKA
ROZETKA is the largest and most recognizable marketplace in Ukraine. It has a high level of trust and strong logistics. It is ideal for quickly covering the domestic market.
Coverage region: Ukraine.
It receives approximately 40–55 million visits per month.
Main categories: Electronics, home and garden, household appliances, children's goods, and FMCG.
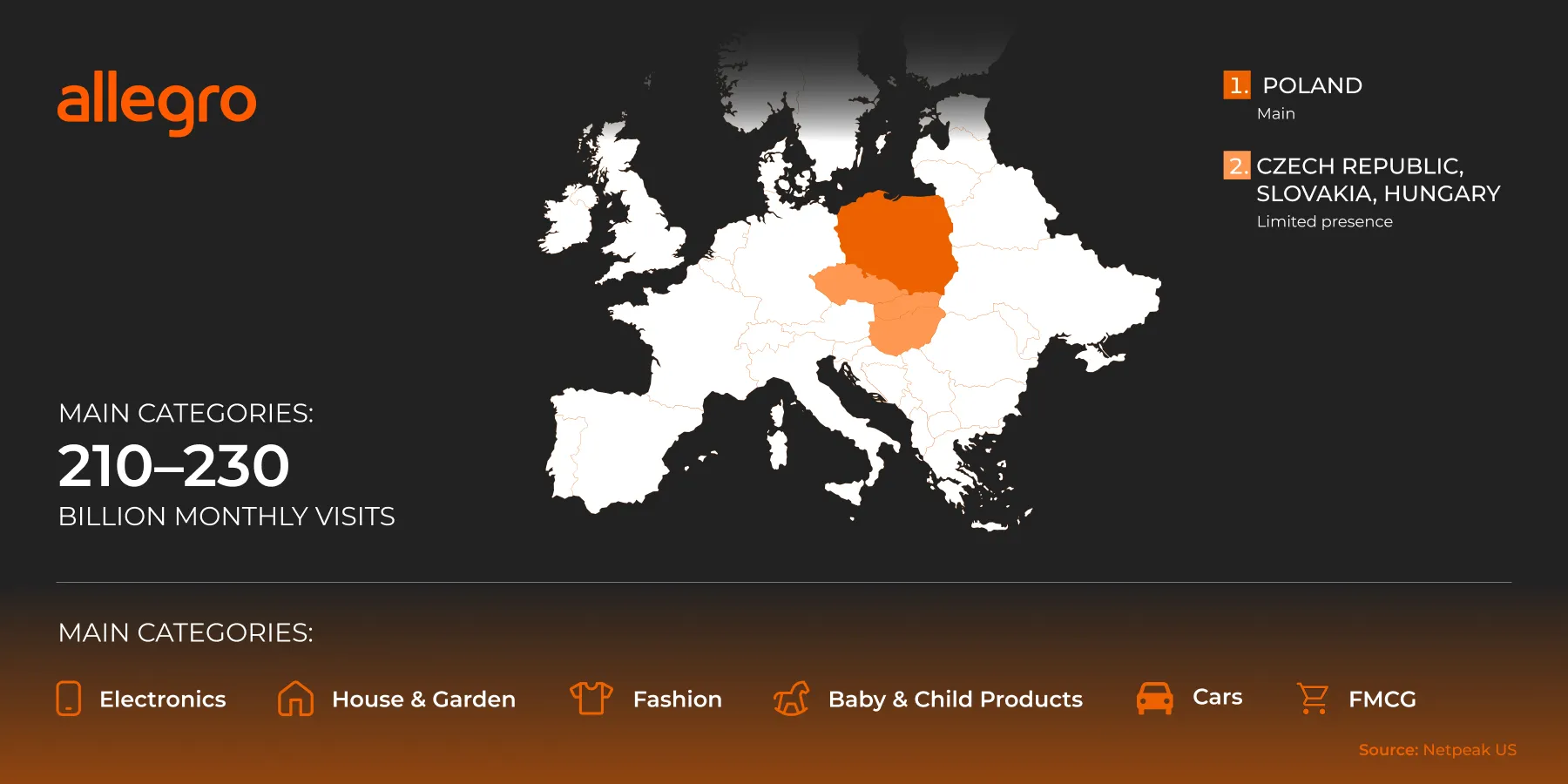
Allegro
Allegro is the absolute leader in Polish e-commerce. Customers are very sensitive to price and delivery terms. There is high buyer trust, strong Allegro Smart logistics, and fierce competition in the top categories.
Coverage regions:
-
Poland — the dominant market.
-
Partially: the Czech Republic, Slovakia, and Hungary.
There are approximately 210–230 million visits per month.
Main categories: Electronics, home and garden, fashion, children's goods, cars, and FMCG.
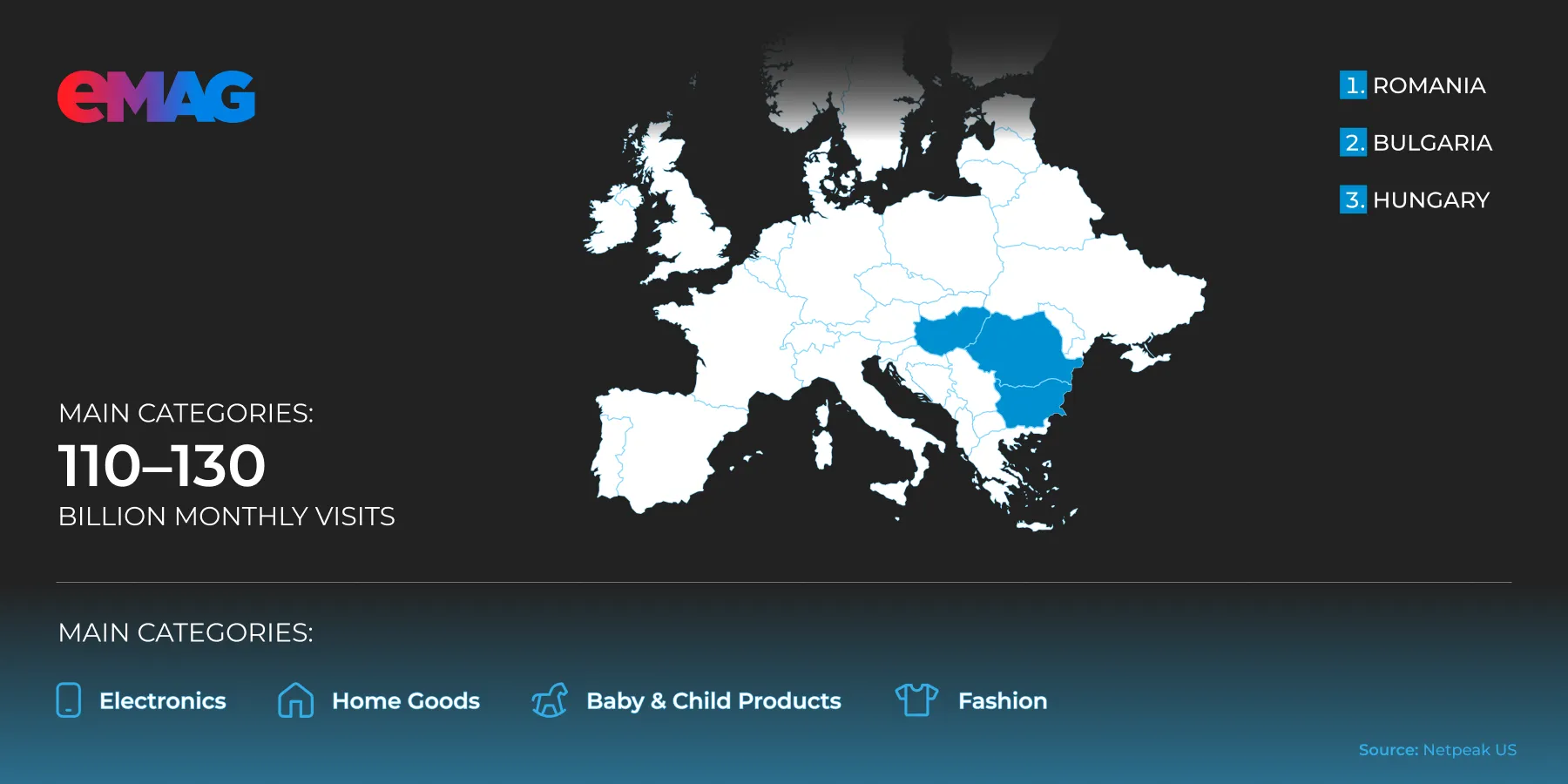
eMag
eMag is the leading marketplace in Romania and one of the top marketplaces in Eastern Europe. While it is ideal for expanding sales in the region, it requires high service quality and fast order fulfillment.
Coverage regions:
-
Romania.
-
Bulgaria.
-
Hungary.
There are approximately 110-130 million visits per month.
Main categories: Electronics, home appliances, home goods, children's goods, fashion.
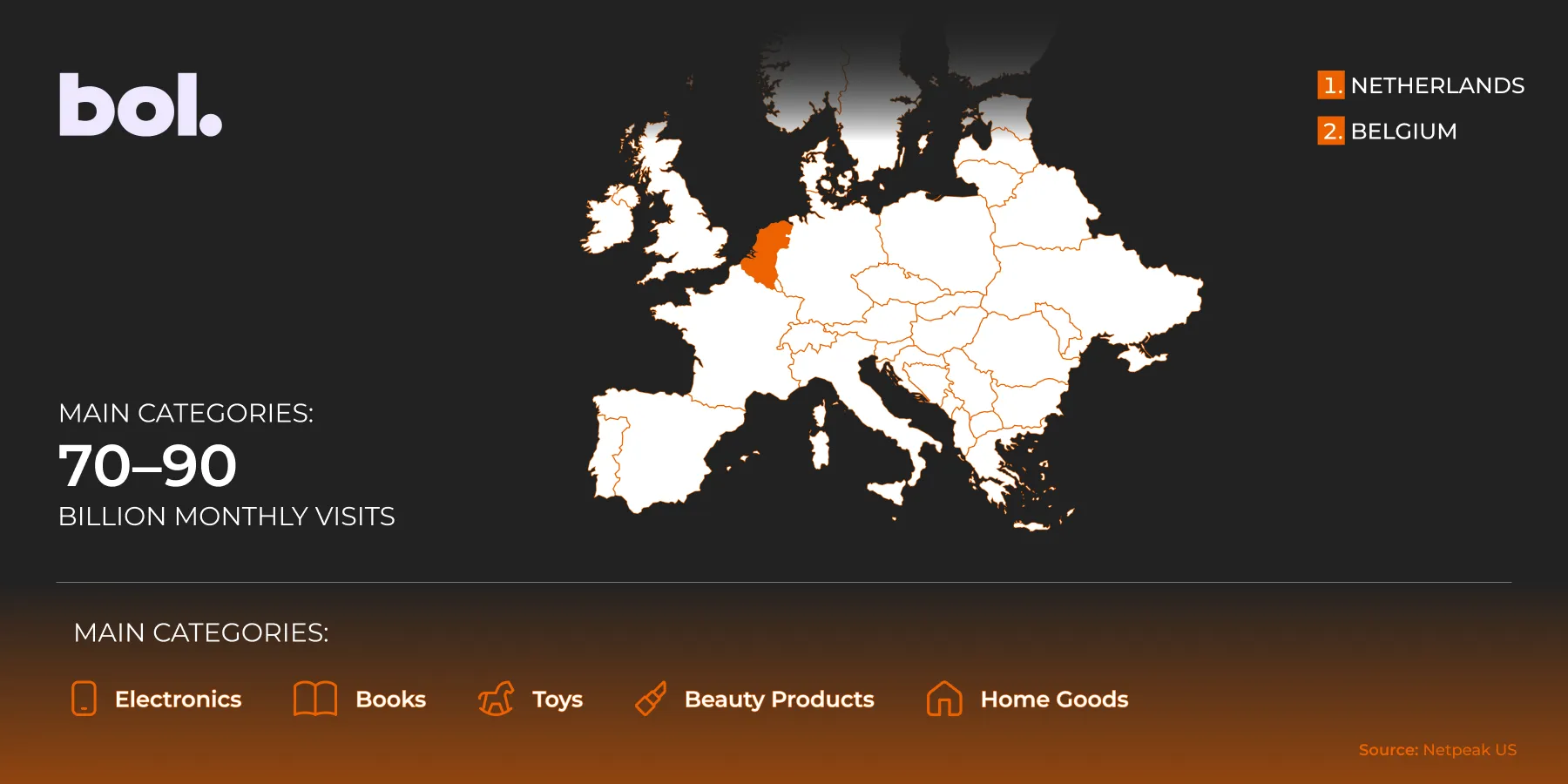
Bol.
Bol. is the largest marketplace in the Netherlands and Belgium. It has high standards for product descriptions, delivery, and customer service. There is little dumping, but high brand standards.
Coverage regions:
-
The Netherlands.
-
Belgium.
There are approximately 70–90 million visits per month.
Main categories: Electronics, books, toys, cosmetics, and home goods.
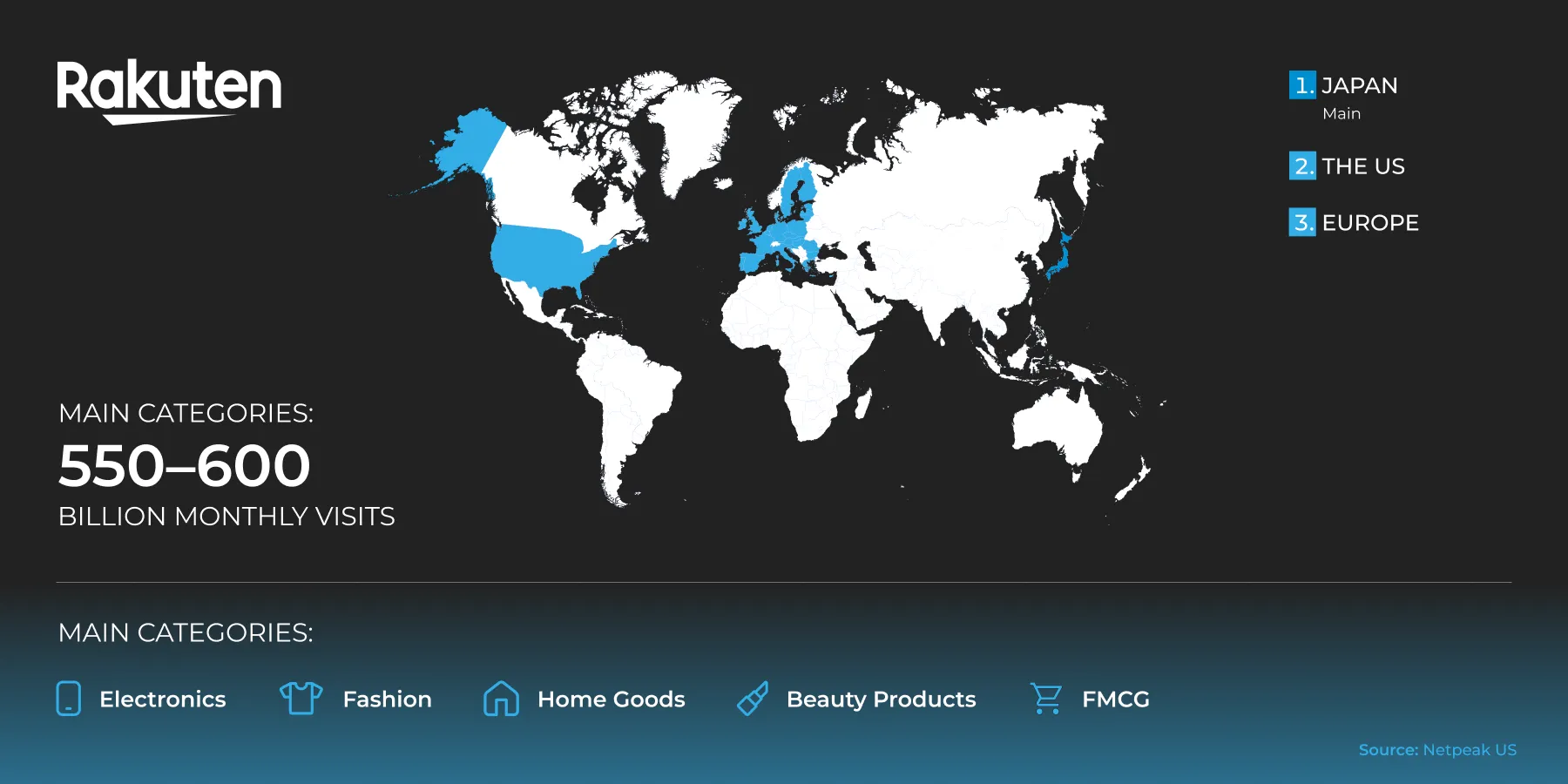
Rakuten
Rakuten is one of Japan's largest marketplaces. It is a closed, highly localized market. To participate, you need a Japanese legal entity or a local partner, content and customer support in Japanese, and compliance with local rules and standards. Buyers have high purchasing power.
Coverage regions:
-
Japan.
-
Scaling to the US and Europe.
There are approximately 550-600 million visits per month.
Main categories: Electronics, fashion, home goods, cosmetics, and FMCG.
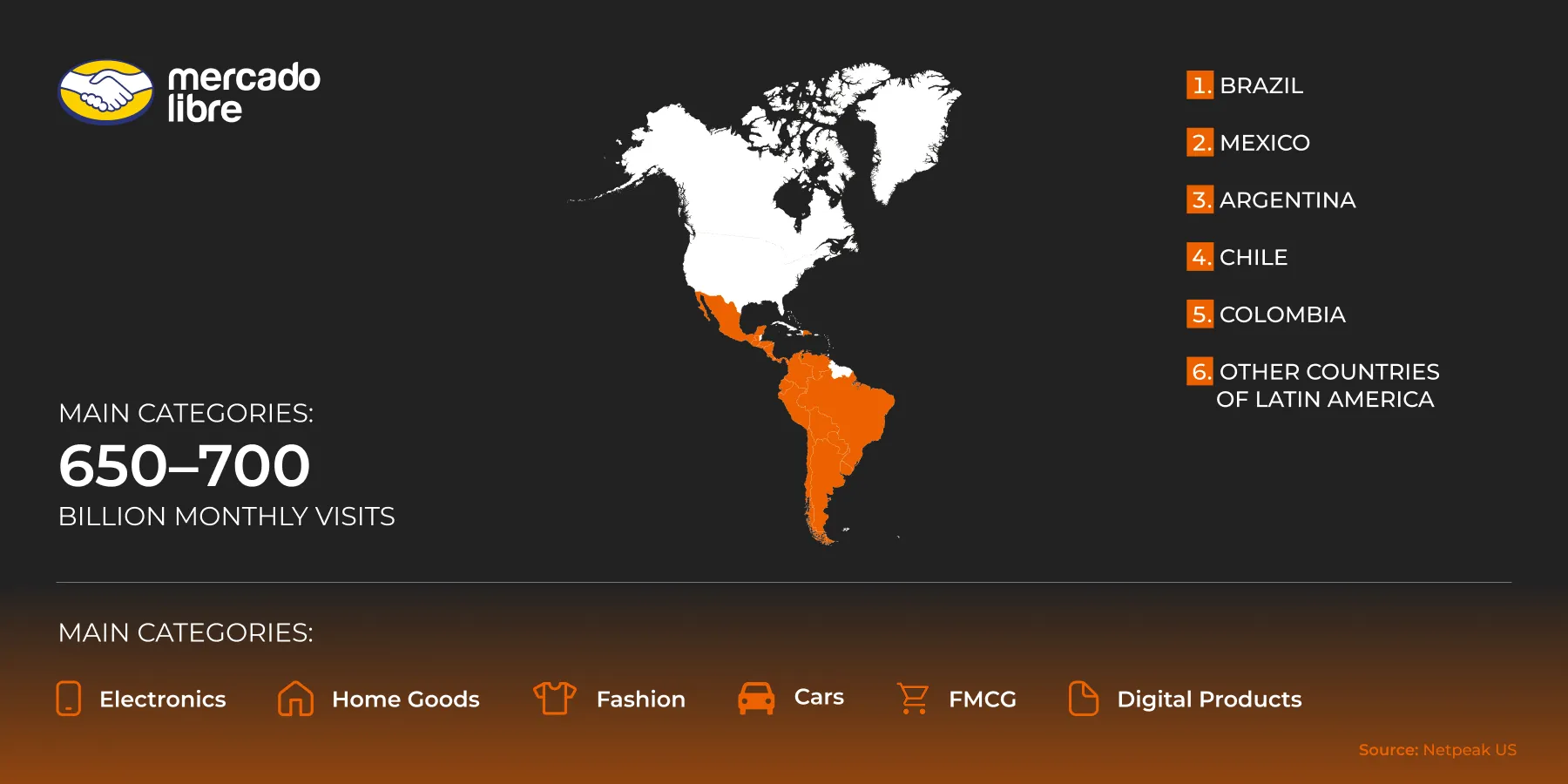
Mercado Libre
Mercado Libre is Latin America's leading marketplace. It has its own logistics system, Mercado Envíos, and payment system, Mercado Pago. There is high demand, but the logistics and government requirements are complex.
Coverage regions: Brazil, Mexico, Argentina, Chile, Colombia, and other Latin American countries.
It receives approximately 650–700 million visits per month.
Main categories: Electronics, home goods, fashion, automotive, fast-moving consumer goods (FMCG), and digital services.
Before You Jump In: Tips for Entering Marketplaces
The beginning often seems simple. You register an account, upload products, and launch an advertising campaign. Trouble usually starts when companies jump in without a strategy. These simple steps might look obvious, but they make a huge difference early on.
-
Analyze the niche.
Instead of registering an account first, start by analyzing demand and the competitive landscape. The same product may sell well on one marketplace but poorly on another.
What to check:
-
The volume of demand in the category.
-
The number of active competitors.
-
Price ranges.
-
The format of the top listings.
-
The presence of advertising and promotions among competitors.
It is important to understand not only if there is demand, but also if there is room for a new seller with your price, brand, and delivery terms.
-
Choose products that are best suited for the marketplace.
Not all products in your range are equally suitable from the start. A common mistake is launching the entire line at once. For the initial launch, it is better to select products that:
-
Products with simple logistics.
-
Goods without complex certification.
-
Items that offer clear value to the buyer.
-
Products for which you can offer competitive prices or configurations.
The marketplace is not a place to test everything at once. It is a place for a focused launch.
-
Buy from your competitors.
One of the most valuable yet underrated steps is to become a buyer yourself. This gives you a clear understanding of what the customer sees, rather than what analytics show. Pay attention to:
-
Packaging quality.
-
Delivery speed.
-
Customer communication.
-
Accuracy of product descriptions.
-
After-sales service.
Identify your competitors' weaknesses and improve upon them rather than copying their mistakes.
-
Choose a sales model.
Before you begin, clearly define your sales strategy. This will directly affect your margin, scaling, and operational load. The most common models are:
-
Sales from your own warehouse.
-
Through a marketplace fulfillment service.
-
Cross-border: A model involving the delivery of goods between different countries.
-
The B2B or wholesale format.
There is no universal model. It is important to choose a model that suits your resources, team, and financial goals.
-
Create content before launching, not after.
On marketplaces, content sells. If your listing is weak, advertising will only accelerate the drain on your budget. Before launching, you should:
-
Optimize titles and descriptions for internal search.
-
Prepare high-quality photos, videos, and infographics.
-
Fill in all product attributes.
-
Clearly explain the product's unique features and value.
A well-prepared listing can generate sales without advertising initially.
-
Plan advertising as a growth tool, not a way to become wealthy quickly.
Advertising on marketplaces is a scaling tool and an investment, not a way to "save" a weak product or listing. Initially, it is necessary for:
-
Testing demand.
-
Collecting initial sales and reviews.
-
Analyzing key queries.
Launch advertising after basic preparation, not instead of it.
-
Allow time for testing.
The marketplace is not a story about instant results. The first one to three months are a period of testing, adjustments, and learning. Important:
-
Don't jump to conclusions after the first few weeks.
-
Analyze data, not emotions.
-
Optimize gradually; don't change everything abruptly.
A systematic approach almost always yields better results than aggressive actions without a strategy.
Zero-Budget Ways to Promote on Marketplaces
Before you put budget into advertising, it’s smart to use the free ways to promote your products — and most platforms have plenty of them.
SEO (Search Engine Optimization for Marketplaces)
Internal SEO is the basis of free traffic. Platform algorithms analyze how well a product matches a buyer's search query and how well it converts.
-
Before launching advertising, it is important to optimize keywords, the description card logic, and its completeness.
-
The title and description should be understandable to both the algorithm and the buyer.
-
Use the main keyword in the title, and clearly explain the product's value, purpose, and differences from competitors in the description. Overloaded or formal texts reduce conversion.
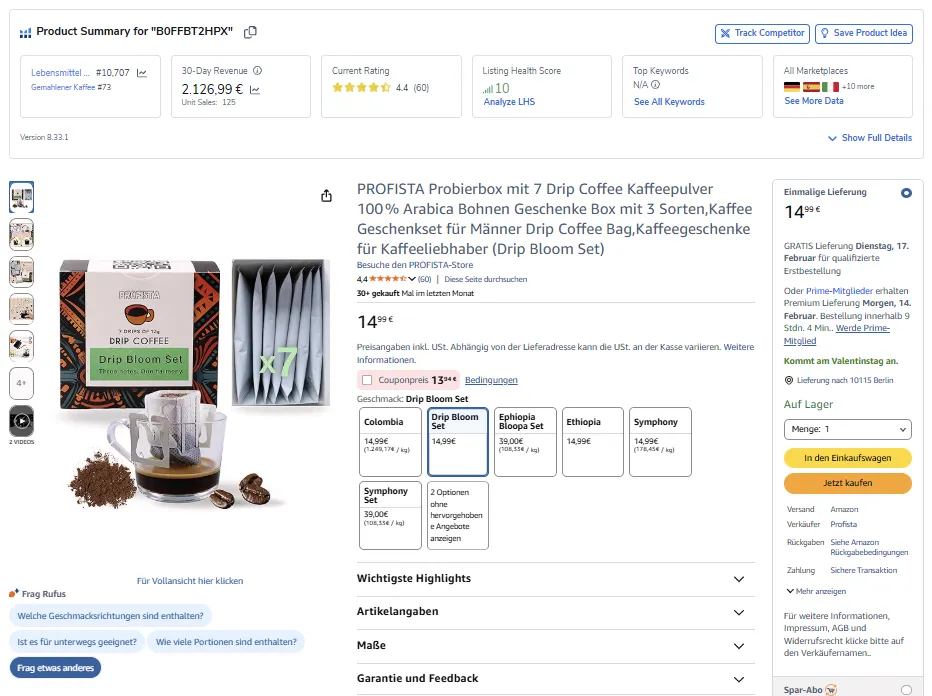
Here is an example of an SEO-optimized listing that generates sales without advertising. Over the last 30 days, it received 151 orders worth €2,000
Storefront
A storefront is a branded page for a seller or store on a marketplace. It builds trust, increases brand recognition, and brings the entire product range together in one logical space. For brands, the storefront often becomes a source of repeat purchases.
-
An attractive storefront has a clear structure, high-quality banners, logical navigation, and clear positioning.
-
Visual elements should emphasize the products' key advantages and simplify the buyer's decision-making process.
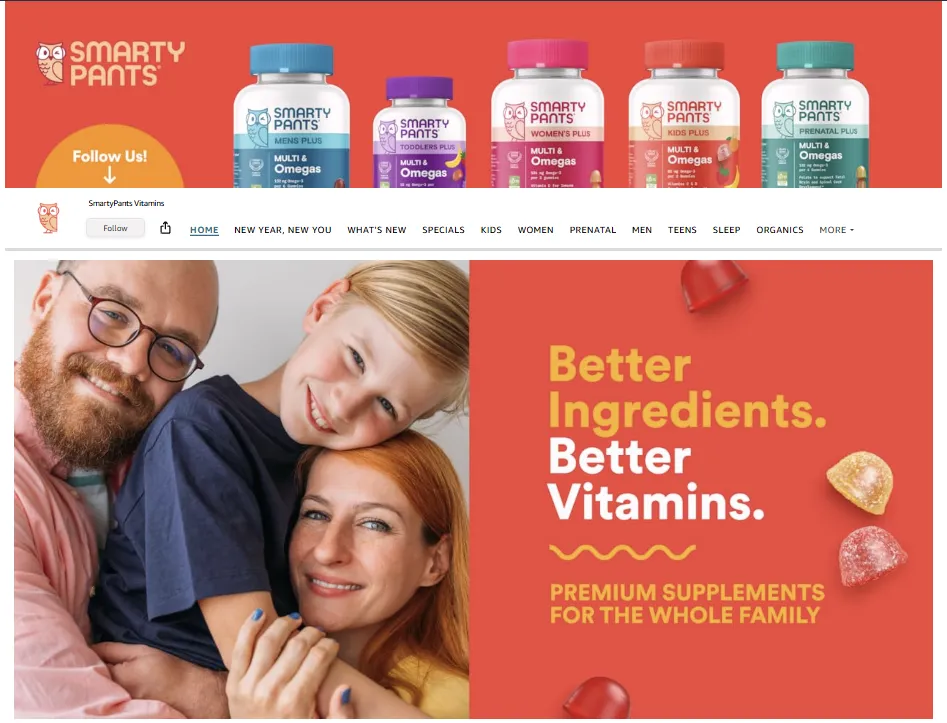
One example is the Amazon Brand Store for Panty Pants, which sells vitamins and dietary supplements for the whole family
Reviews as a Growth Factor
Reviews directly impact buyer trust and product visibility within the catalog. A few relevant reviews can significantly increase the conversion rate of a new listing and accelerate organic sales growth.
-
You can obtain reviews without violating marketplace rules by providing quality service, clear packaging, expressing gratitude after the purchase, and communicating with customers in an unobtrusive manner after delivery.
-
The important thing is to avoid directly encouraging ratings or manipulating reviews.
Negative reviews provide an opportunity to demonstrate your brand's commitment to customer satisfaction. A calm, reasoned response and a willingness to solve the problem can increase trust more than a perfect rating without feedback.
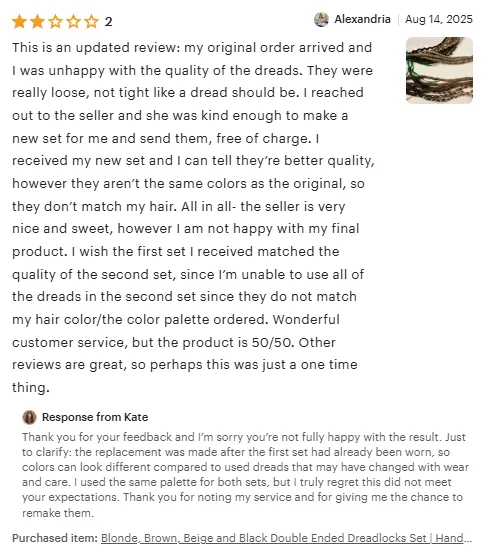
Here's an example of how a negative review on Etsy showcases a brand's customer focus
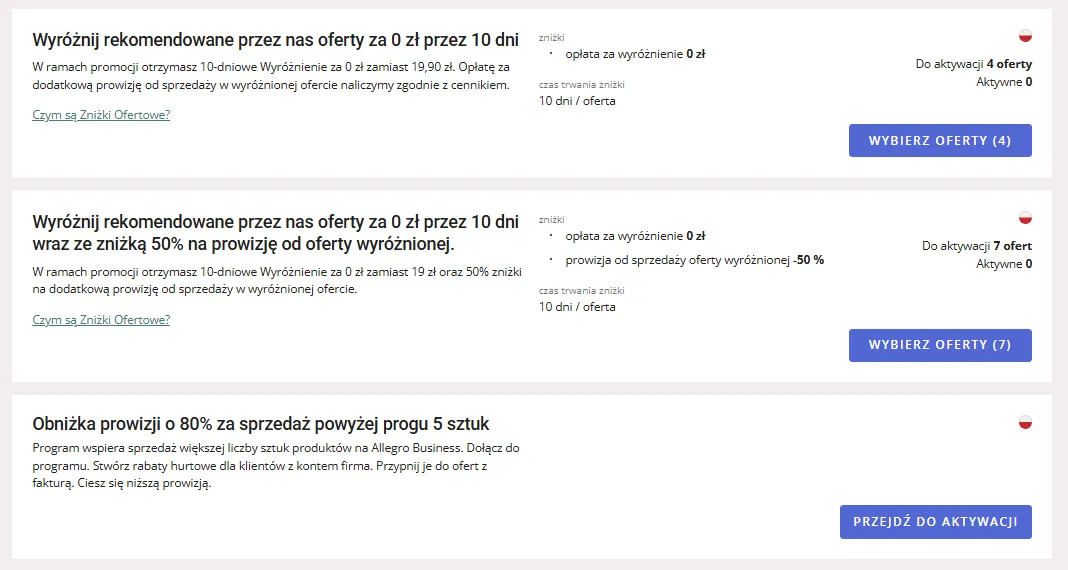
Promotions and Discounts
They are one of the easiest ways to gain additional visibility within the marketplace for free. Temporary discounts, product bundles, and participation in internal platform promotions help drive initial sales and test demand more quickly.
-
An effective promotion should be time-limited, understandable to buyers, and cost-effective for businesses.
-
Promotions are best used to launch a product, accelerate turnover, or clear inventory rather than as a permanent strategy.
Sellers on Allegro use discounts to gain additional visibility for their products
Pay to Play: Paid Promotion Tools on Marketplaces
Paid tools help you grow faster once your listings are properly optimized. They let you control visibility, test demand quickly, and compete for high-value searches when organic traffic isn’t enough.
Advertising
Marketplace advertising tools display products directly in search results, categories, or on competitors' pages.
-
The most commonly used tools are keyword campaigns, automated data-collection campaigns, and product listings targeting specific products or categories.
-
Advertising is most effective when the listing is ready for conversion.
Here is an example of the effective use of Amazon Ads in the arts and crafts niche
Initially, it is important not to try to cover everything at once. It is more effective to launch advertising with a limited budget, test key queries, and gradually scale only the campaigns that generate sales. Bid control and regular budget optimization directly affect profitability.
Marketing Support from the Marketplace
Many platforms offer additional promotional opportunities, including seasonal sales, special selections, brand zones, and promotional campaigns. These paid or conditional tools provide a short-term but strong surge in visibility.
An example of recommended marketing activities for Allegro.pl sellers
Special Programs and Offers
Loyalty programs, brand support, exclusive offers, and partnership formats with the marketplace will help your business stand out from the competition. These tools are especially effective for launching new products and scaling up existing ones.
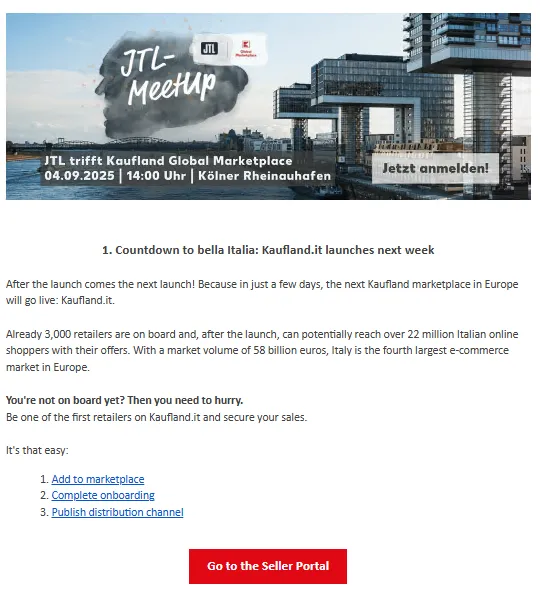
Kaufland offers sellers the opportunity to grow by expanding into Italy
Key Takeaways
-
A marketplace is a platform with ready-made demand. Your job is to compete for visibility and buyer trust, not for traffic itself.
-
Marketplaces work differently, so you can’t use the same playbook everywhere.
-
Global marketplaces help you sell internationally fast, but they are highly competitive and require consistent effort and investment.
-
Local marketplaces often convert better and let you start selling faster because they are built for their specific market.
-
Successful entry into a marketplace requires researching your niche, selecting the right products, assessing unit economics, and defining your sales model.
-
Free promotion methods, such as SEO, reviews, and basic listing optimization, form the foundation of sales.
-
Paid promotion can speed up growth, but it only works well if your content, pricing, and analytics are already in good shape.
-
Success on marketplaces comes from a strategic approach to sales and promotion, not one-off actions.
Related Articles
Home Service Marketing: 8 Winning Strategies for 2026 (Checklist Inside)
Home service marketing made simple: 8 proven strategies for 2026 to rank for “near me” searches, generate emergency leads, and turn urgent calls into loyal, repeat customers — plus a practical checklist.
SEO for HVAC Companies: 12 Mistakes That Make Your Business Invisible (+Best Practices Template)
SEO for HVAC companies explained: local ranking basics, 12 costly mistakes to avoid, multichannel best practices, and a practical self-audit checklist to help you win more local jobs.
Plastic Surgery Marketing: 11 Strategies to Make Your Practice Visible Online
Discover 11 practical plastic surgery marketing strategies to boost online visibility, build trust, and turn website visitors into real consultations.