The main goal of Google Ads targeting is precision. It determines who sees your ads, when they see them, and under what conditions. Targeting helps reach your people who are most likely to care about your message.
Think of it like Katniss in The Hunger Games. When the judges ignored her, she shot the apple out of the roasted pig's mouth, scaring them all to death. That single shot made them pay attention.
Of course, you don't need to scare your customers, but you do need to ensure your message reaches the decision-makers. This guide to Google Ads targeting can help with that. Aim for the right audience, and you’ll get more sales, more customers, and better results for every dollar you spend.
-
What Is Google Ads Targeting
-
How Google Ads Targeting Works: Strategy, Not Luck
-
Pick the Right Weapons: Types of Google Ads Targeting
-
Target Smarter, Not Harder: Best Practices
-
Your Roadmap to the Right Targeting Strategy
-
FAQ
What Is Google Ads Targeting: Choosing the Right Mark in the Arena
How does Google Ads work? It helps your business show up in front of the people who are looking in search results for what you offer right now — or checking out websites, videos, and apps related to your products or services.
Optimized targeting is the secret sauce that makes it work. Instead of showing your ad in paid search to everyone online, it helps you reach the people who really care — based on their age, location, interests, searches, device, and more.
Smart marketing is about targeting the right audience at the right moment.
How Google Ads Targeting Works: Strategy, Not Luck
To have good results, you must treat targeting like a science. That means looking at the data, figuring out who your best customers are, and choosing the right mix of age, location, interests, keywords, and placements to reach them.
Remember — you’re not alone in this arena. Competitors are everywhere, and every impression counts.
Smart targeting means your money isn’t wasted on people who aren’t interested. The more of the right people see your ads, the more clicks, and the more they buy. Well-targeted campaigns make every dollar count and turn your ads into actual results for your business.
Pick the Right Weapons: Types of Google Ads Targeting
Think of Google Ads targeting as fishing. Instead of casting a net in the middle of the ocean, you use the right bait in the right spot. Each targeting type provides a different "fishing strategy."
Google Display Targeting
Your ads appear on websites, apps, or YouTube videos that your audience visits in the Google Display Network. You can choose where and to whom your ads show — based on people, placements, demographics, interests, or topics.
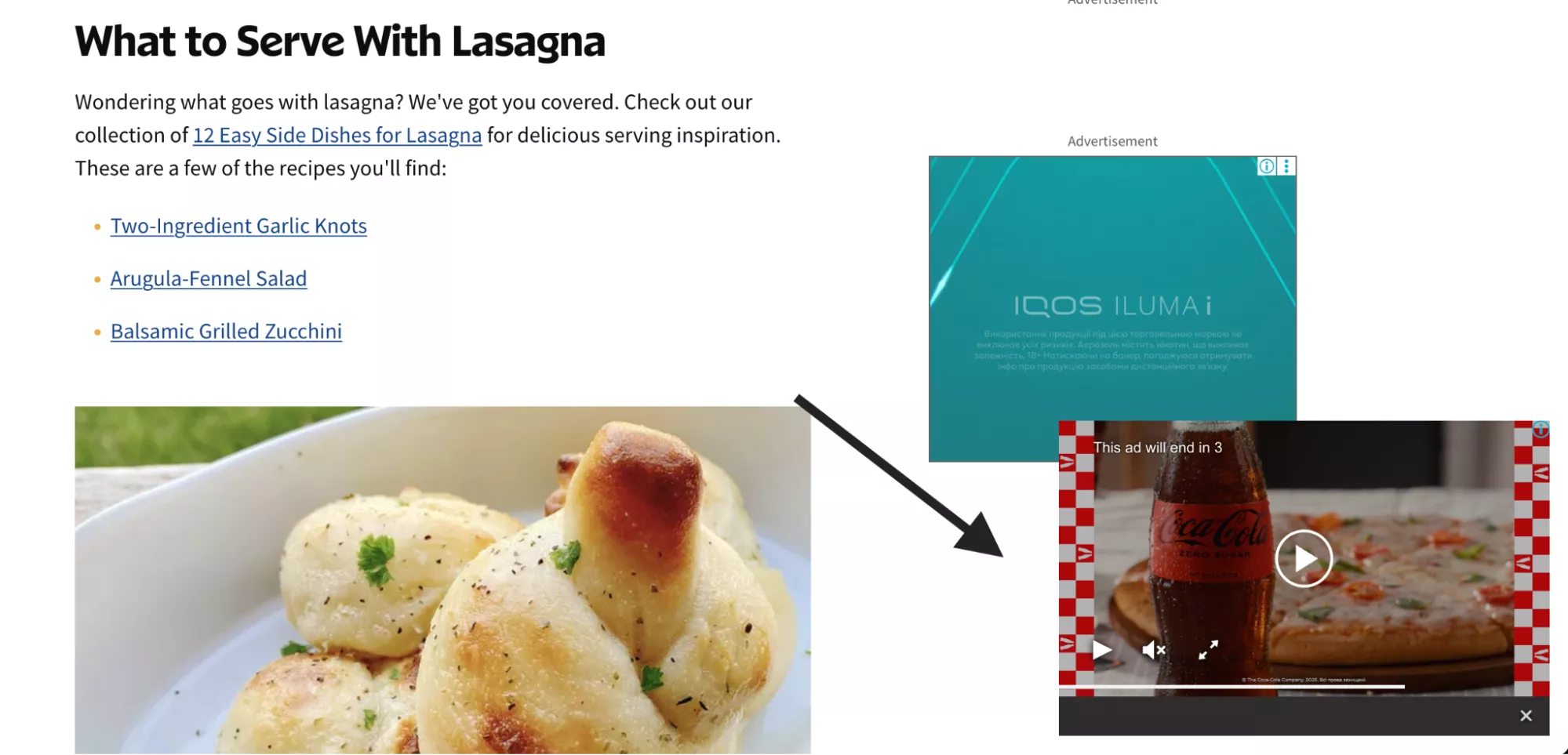
For example, Coca-Cola shows ads on recipe sites, which makes perfect sense. It reaches people in the right context: users are already thinking about food and beverages, which naturally aligns with Coca-Cola’s product.
Instead of waiting until someone searches for “soda” or “soft drinks,” the brand shows up earlier in the decision-making journey, subtly influencing purchase intent.
You want to show your ads on relevant websites, apps, or YouTube videos where your audience spends time. To do it right, you need:
-
Decide who your audience is (age, interests, location, device, etc).
-
Pick placements: websites, apps, and content categories, or let Google choose it for you.
-
Design banner or video ads that grab attention.
-
Decide how much you want to spend per impression or click.
-
Track performance.
Google Search Targeting
Ads appear when someone searches for specific keywords on Google. It is smart because these people already want what you’re offering.
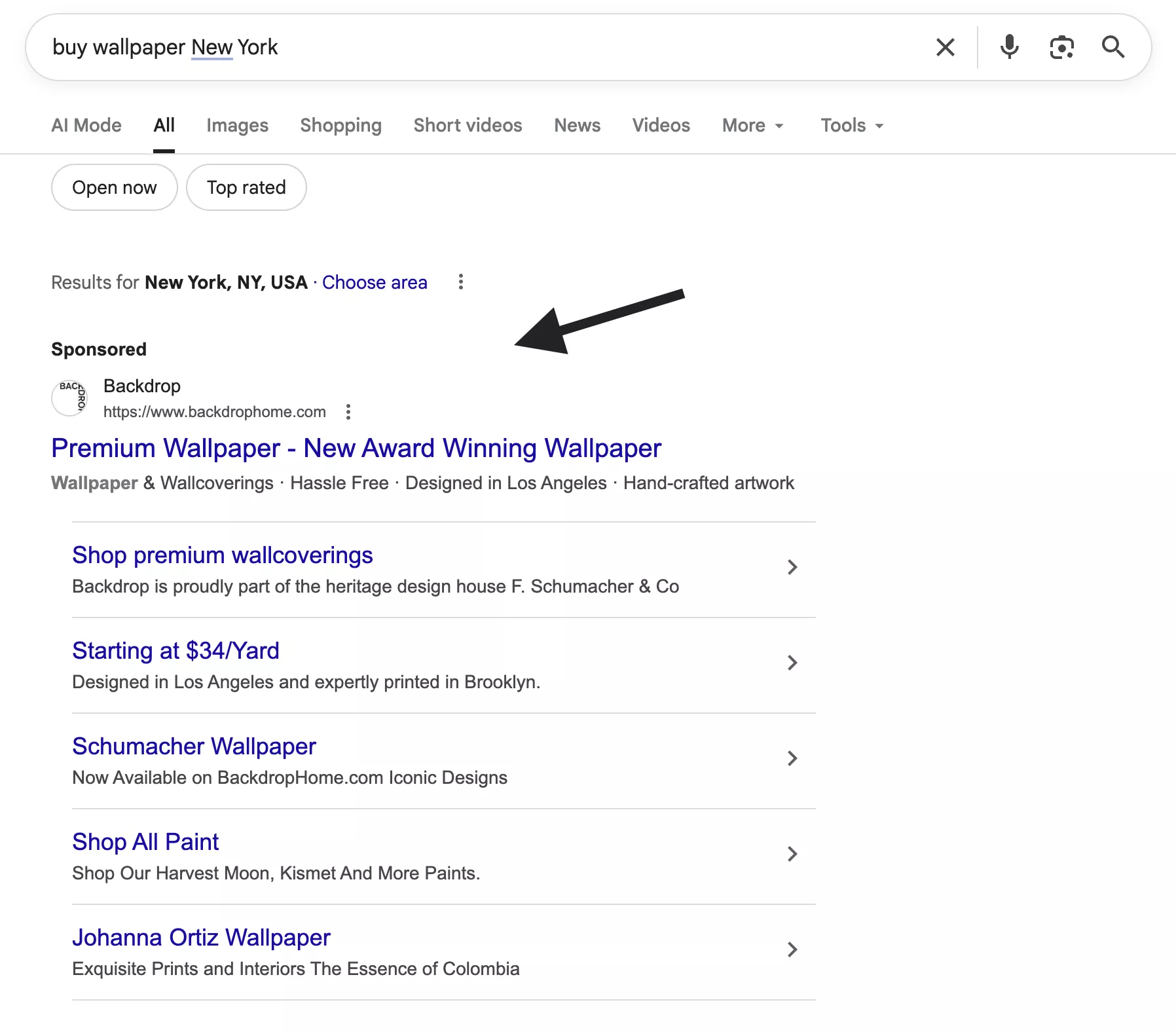
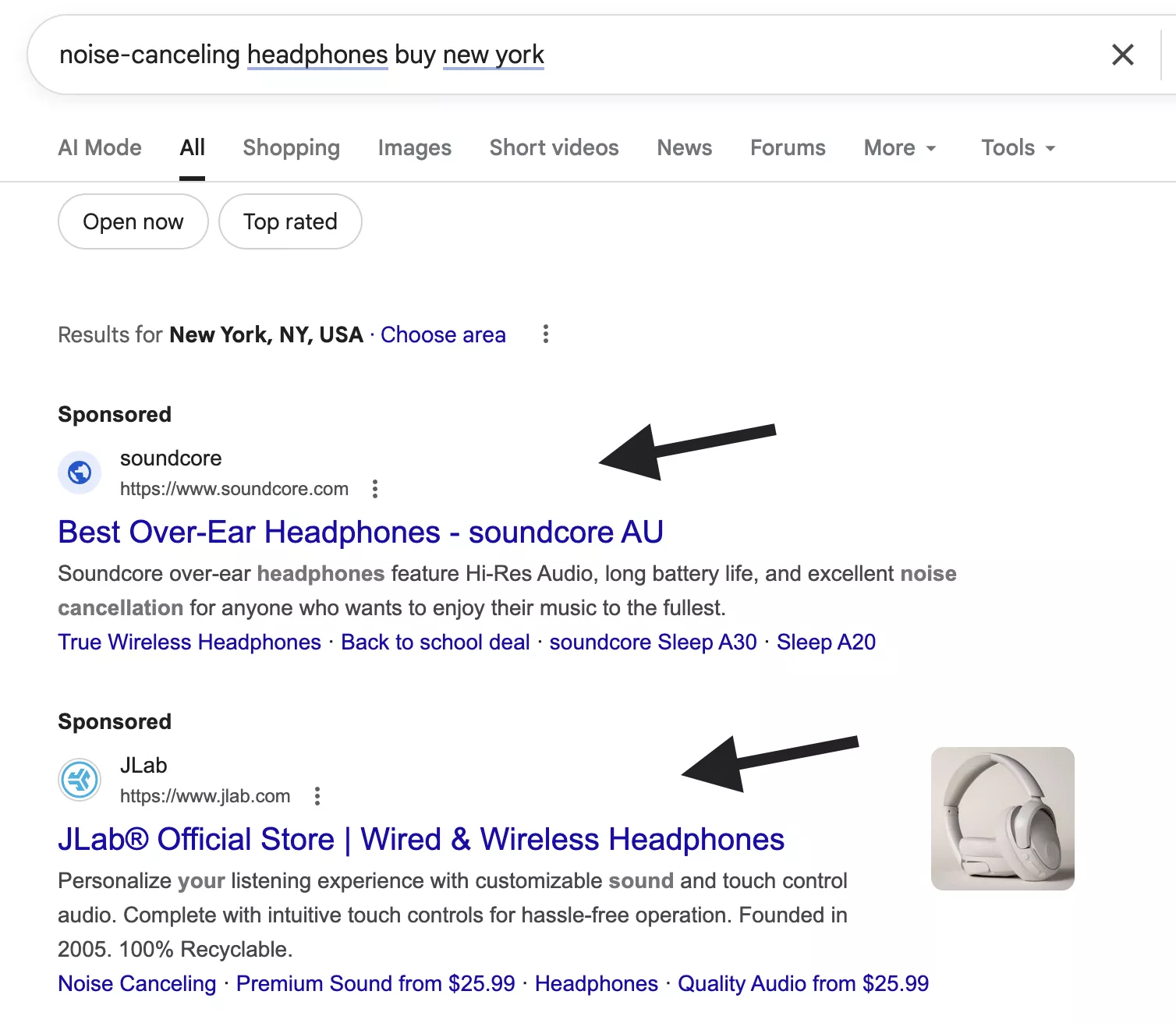
For example, if someone searches “noise-canceling headphones buy New York,” your ad pops up. You’re reaching intent-driven customers — people who are actively looking, not just browsing.
To do it right, you need:
-
Do keyword research to identify the terms your potential customers are likely to type in (broad, phrase, or exact match).
-
Choose demographics, location, and devices of your audience.
-
Write compelling ad copy.
-
Decide your cost-per-click (CPC) and daily ad spend limits.
-
Launch and optimize.
Demographics Google Ads Targeting
Think of your ad as a custom-tailored suit — it fits perfectly when made to your specifications. Similarly, your ad will work best when it’s targeted to the right age, gender, parental status, and income level.
Age
It’s showing your ad to people in certain age groups. For example, a trendy sneaker brand might focus on 18–34-year-olds because they can still afford fashion and haven't spent all their money on healthcare yet.
Start with the age group that fits your product, but try a few different ranges to see which one actually clicks and converts. Maybe someone going through a midlife crisis will want your sneakers? Who knows? ?
Gender
Gender Google Ads Targeting lets you show your ads to men, women, or everyone. For instance, a men’s beard kit would primarily target men, whereas a lingerie brand would focus on women.
But, as you know, gender is a social construct. You need to be sure that this division really makes a difference. Otherwise, showing your ad to everyone will give you more potential customers.
Parental Status
This type of targeting helps you reach parents — and even narrow it down by the age of their kids. For example, a stroller company can show ads to parents with toddlers under 5.
Many family-oriented products, such as toys and children's educational apps, depend on age. Children grow quickly, so parents need to find new ways to entertain little guys.
Household Income
It helps to show your ads based on how much money people are likely to earn. For example, a luxury watch brand owner should focus on the top 10-20% income bracket.
This targeting method is useful for higher-end products that only lucky people can afford.
Topic Google Ads Targeting
You can display your ads on specific websites or apps. For example, if you sell online games for kids, you can choose to post ads only on sites where children like to spend time.
The kids will see your ad and want what you're selling, and tired parents will give in after 15 minutes of nagging. It really works!
Placement and Device Google Ads Targeting
With Placement Targeting, you can choose exactly where your ad shows up. For example, if you sell fitness gear, you can place your ad directly on popular workout blogs or YouTube fitness channels. If someone is already there, it means they actually play sports and don't just say they're going to start on Monday like everyone else.
With the Device Targeting campaign, you decide which devices your ad appears on — desktop, tablet, or mobile. For example, a food delivery app targets mobile users because that’s where people order food.
Keyword Google Ads Targeting
You need to use keyword research to figure out what your customers type into Google when they want something like yours.
-
A gym owner might imagine people search for “fitness center memberships”, but most people actually type “cheap gyms near me”.
-
A bakery may think of “artisanal bread”, while customers search “fresh bread delivery”.
There are three types of matches you can use. Each type is relevant in its own way and helps you achieve different goals.
|
How It works |
Example |
Result |
|
|
Broad Match |
It shows your ad when someone searches for your keyword or something related. |
For example, if your keyword is “running shoes”, ads could also appear for “best sneakers” or “sports footwear”. |
You reach a wide net of people, but some may not be ready to buy. |
|
Phrase Match |
It shows your ad when a person types your keyword phrase with extra words before or after. |
For example, the keyword “running shoes” could match “best running shoes for women” or “cheap running shoes online”. |
It helps to balance reach and relevance: you still get variety but fewer random conversions. |
|
Exact Match |
It shows your ad only when the search is very close to your chosen keyword. |
For example, the keyword “running shoes” would trigger only searches like “running shoes” or “buy running shoes”. |
Only the most qualified people see your ad. Best for tight budgets. |
Audience Targeting
It lets you show your ads to people based on their interests, habits, and past behavior.
-
Affinity Audiences: Google groups people into audiences like “fitness enthusiasts” or “frequent travelers”
-
In-Market Audiences: Google identifies people who are close to making a purchase. For example, if you sell headphones, people searching for "best noise-canceling headphones” will see your ad.
-
Custom Audiences: You can also create custom Google Ads audiences based on what people have already done, like visiting your website or watching your videos.
Geographic Targeting
You can choose the locations where your ads appear — countries, cities, neighborhoods, or even a radius around a store. For example, a coffee shop in Brooklyn needs to target ads only to people in or near Brooklyn. Simple logic!
It’s so useful for local businesses, events, or region-specific promotions. No point spending money on someone hundreds of miles away.
Retargeting: Remind People Who Already Showed Interest
You can show ads to people who have already visited your website, used your app, or interacted with your brand. For example, someone looked at a pair of running shoes on your site but didn’t buy — retargeting shows them an ad to remind them.
Retargeting is like gently nudging someone who almost bought — boosting sales without reaching cold audiences. It often gets some of the highest ROI because the audience already knows your brand.
Target Smarter, Not Harder: Best Practices
Here are a few tips you can actually use to save your money:
-
Exclude what doesn’t matter. For instance, if you sell premium software, exclude users searching for free alternatives. It doesn’t make sense to pay for clicks from people who’ll never buy from you.
-
Combine targeting options. You have many audiences; you just need to know them. For example, a car dealership could target in-market audiences for SUVs + parents with kids within a 20 km area.
-
Exclude past converters (if it makes sense). An ecommerce store that sells mattresses doesn’t need to keep advertising the same mattress to the same customer, but they could run ads later for sheets, pillows, or bed frames.
-
Use demographic filters carefully. Test age, gender, and household income filters — but only exclude if you’re sure your product isn’t for that group.
Your Roadmap to the Right Targeting Strategy
Think of targeting as choosing where to open a new store. You need to pick a location with the most potential customers. Google Ads works the same way.
Step 1: Start with the Outcome in Mind
Think carefully about what the main goal of your business is right now.
-
More sales right now? You need to use in-market audiences or keywords to attract people who are ready to buy.
-
To build awareness? It’s all about affinity audiences or broad targeting. Attract people who fit your ideal profile. It’s not a big problem if they’re not ready to buy yet.
-
Repeat customers? Retargeting is your first choice to reach people who have already visited your site.
Step 2: Understand Who You’re Talking To
Ask yourself: Who is buying your product? What is their age and gender? Do they have children? How much money do they earn? Where do they live? What are their hobbies?
It's better to do some research to find out who your customers are, because you might be surprised.
Step 3: Let Your Product Guide Your Targeting
It's all about your specific product. If you’re a local service, such as a plumber, use geo-targeting and exclude other areas. If you sell luxury products, use income- and interest-based targeting. For everyday products like coffee or clothes, keep the targeting broad to reach more people.
Step 4: Try, Learn, Repeat
Don't overthink it at first. Launch ads, collect data, and identify which groups convert. Then, focus on what works.
FAQ
How does targeting work in Google Ads?
Targeting decides who sees your ads and where. Instead of showing your ad to everyone, Google lets you focus on the people most likely to care — based on keywords, interests, demographics, location, devices, and more.
It’s like putting your message in front of the right eyes at the right time.
How to target an audience on Google Ads?
You can target people in multiple ways:
-
Demographics: Age, gender, parental status, income
-
Keywords: What people search for
-
Topics & placements: Websites, apps, or YouTube channels related to your product
-
Audience types: Affinity, in-market, or custom audiences
Start small, test different audiences, and see who responds best — then refine for better results.
What are the targeting options in Google Ads?
The main options include:
-
Google Search & Display Targeting
-
Demographics targeting
-
Topic, placement, and device targeting
-
Keyword targeting (broad, phrase, exact)
-
Audience targeting (affinity, in-market, custom)
-
Geographic targeting & retargeting
Should I use targeting or observation on Google Ads?
-
Targeting: Your ad only shows to the selected audience. Use this when you want precision.
-
Observation: Your ad shows to everyone, but you track performance for certain audiences. Use this when testing or learning which groups respond best.
For beginners: start with observation to gather insights, then switch to targeting for higher ROI.
Related Articles
SEO for Moving Companies: Boston Edition
Local SEO is a highly effective tool to make your moving company known in Boston and attract more quality website traffic. Read how SEO can help you outgrow competitors and top the Google SERP chart in 2026!
Word-of-Mouth Won’t Save Your Moving Company. Here’s How to Actually Streamline Leads [Research & Industry Insider Tips]
Relying on referrals isn’t enough to grow your moving company. Discover proven strategies to diversify lead sources and streamline client acquisition with insider tips.
Electrician Digital Marketing: 11 Tips to Get Your Business on Top
Digital marketing for electricians can be tricky, but it is an indispensable tool for brand visibility. Discover how to leverage digital marketing to get more customers for your electrical company in 2026!